cpu scheduling algorithm
FCFS(FIFS)(FIFO)
First-come First-service /
First-In First-service /
First-In First-out
平均 turnaround time 和 waiting time 較長,
並和進入ready queue的順序有關。
Convoy Effect
Burst Time
\( P_1 \)
24
\( P_2 \)
3
\( P_3 \)
3
SJF(Shortest Job First)
選擇最小 CPU Burst Time的Process先執行Priority scheduler
會將CPU指定給具有最高優先權的Process,
Burst time
Priority
P1
10
3
P2
1
1
P3
2
3
P4
1
4
P5
5
2
內部定義: 外部定義: Priority Scheduling 問題(Starvation)
問題是可能會讓較低優先權的process陷入無限期的等待CPU的地步。solution: Aging Techique (老化技術)
將在os中等候久的process的優先權逐漸提高。
Round-Robin Scheduling
O.S會定義CPU時間配額(Time Quantum)或時間分割(Time Slice)。Multi-processor scheduler
如果每個CPU有獨立的queue,master processor
排班決定、I/O處理以及其他系統的動作都交由一個單一的cpu處理。Real-time system scheduling
hard real-time system
必須在一定量的時間內完成task,
通常要執行的process要到cpu時會附帶描述需要計算的或執行的
I/O時間量。Soft real-time system
要求重要process優先權高於其他process。
有優先權的排班功能,
real-time process必須要有最高優先權,
且優先權不能隨時間遞減。(這個process不能被aging)
response waiting 時間要短。
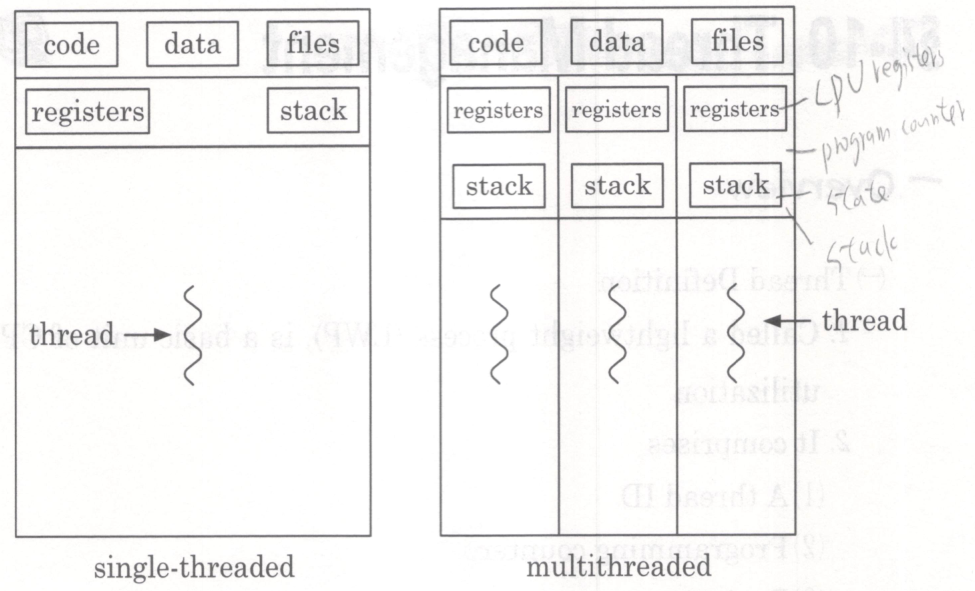
Thread Management
Called a lightweight process(LWP), is a basic unit of
CPU utilization.
It comprises
A thread ID
Programming counter
Register set
Stack
It shares with other thread belonging to the same process
Code section
Data section
Other os resources such as open files and signals.
If the process has multiple threads of control, it
can do more than one task at a time.
Reference
洪逸-作業系統金寶典